Considerations, advantages and disadvantages of micro injection molding
Micro injection molding refers to the injection molding of products with small volume or very high tolerance requirements and tiny overall feature structure. With the development of technology, it has been applied in various fields such as optical communication, computer data storage, medical technology, biotechnology and watch cameras, high-precision gears, medical sensors, etc.
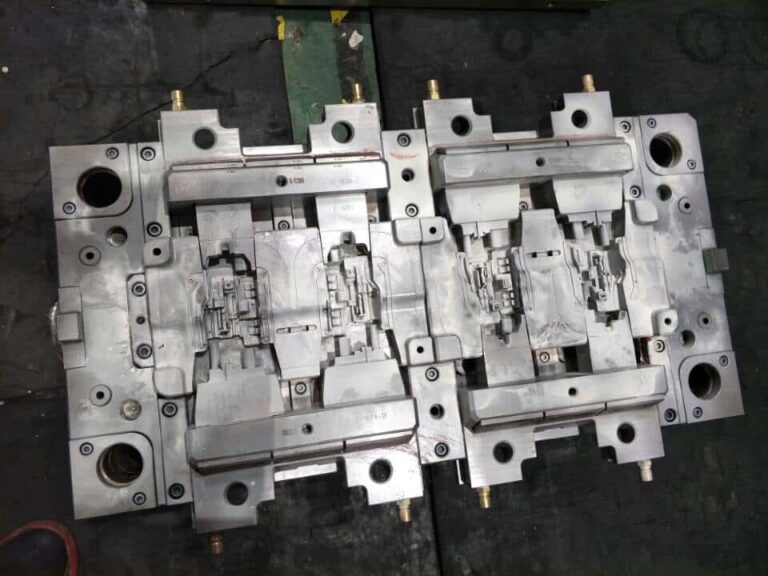
A, micro injection mold design should pay attention to the following.
Heat insulation and thermal insulation of the mold, etc. should be done well to maintain the stability of the mold temperature.
The exhaust system needs to be designed smoothly to prevent the tiny features of the product from scorching and not playing full.
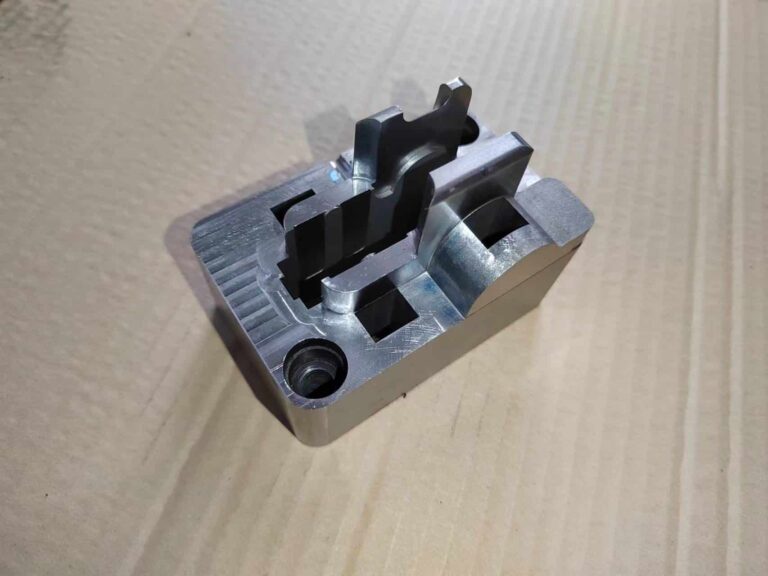
Most of the products of micro-injection molding are small, and the surface of the products cannot be lined up with the ejector mechanism, so the design needs to consider increasing the auxiliary ejector or the side feed glue head to bring out the product structure form.
The size of the product feeding method and the size of the material head need to be designed reasonably to ensure that the product is smoothly played out on the one hand, and to ensure the matching of the injection volume on the other.
Because the product structure is generally small, the processing accuracy is required to be high, and the tolerance design of the workpiece should be reasonable.

Second, the requirements of micro-injection molding equipment
Small plasticizing device should be used, with screw diameter in the range of 12 – 18mm and short screw length, and the L/D ratio needs to be reasonable to avoid material degradation caused by long residence time.
Ensure precise injection volume control and reasonable injection speed, with machines sometimes equipped with separate plungers and screws for metering and injection, with the aim of precise metering of the injection volume and elimination of problems related to material degradation due to shunting and dead space of conventional injection screws.
Multiple controls are possible, for example, i.e., from screw position, but also from filling to holding pressure, depending on the cavity pressure.
The use of switching nozzles, where possible, to avoid flow delays due to high processing temperatures.
Adopt certain image monitoring system to ensure the stability of product removal and prevent mold compression.
Third, micro-injection molding on the injection process requirements
Adopt high speed and high pressure filling method.
Adopting higher material temperature as far as possible within the range of material temperature allowed.
Adopt the higher temperature as possible within the range of mold temperature.
IV. Advantages and disadvantages of micro-injection molding
Advantages: micro-injection molding reduces the number of cavities due to its small size, which is conducive to improving the balance of the mold and increasing the accuracy of product appearance and size; it is easier to control the stability of the mold temperature due to its small size, which meets the requirements of precision molding and also saves the energy required for mold heating/cooling; the mold cost is low and the development cycle is short.
Disadvantages: Large runner volume, sometimes the material in the runner may account for up to 90% of the total injection weight. Also, for micro-injection applications, the material inside the runner is in most cases not recyclable and material waste is more serious. Also, since the surface/volume ratio of micro-injected products is usually very high, the mold must be heated above the melt temperature during injection to prevent early curing, making the production cycle time longer.