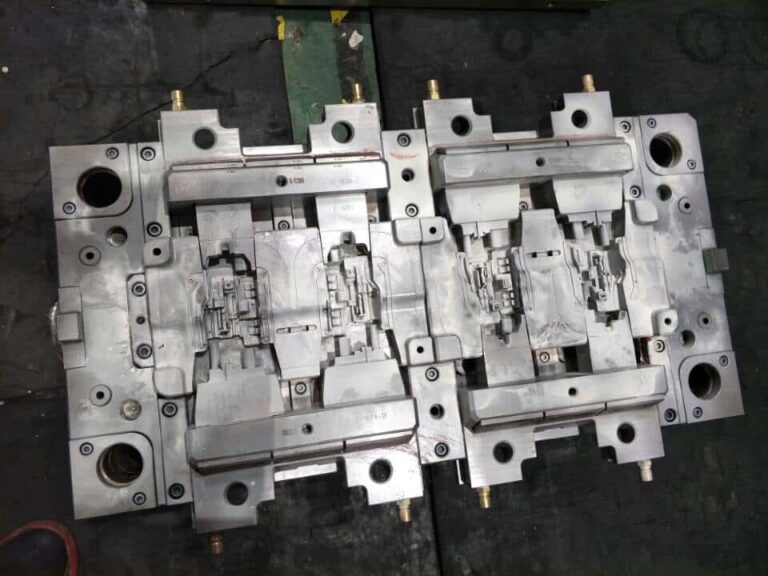
Key points for metal insert design of injection molding products
The thermal expansion coefficients of plastic and metal are 5~10 times different, so when plastic products with metal inserts are cooled, their shrinkage degrees are different. Because the plastic shrinkage ratio is large, they tightly hold the metal inserts. The plastic inner layer around the inserts is under compressive stress, while the outer layer is under tensile stress, resulting in stress concentration.
The following points shall be paid attention to when installing the embedded parts to help reduce or eliminate the internal stress:
A. Plastic parts shall be selected as inserts as far as possible.
B. As far as possible, metal materials with small difference with plastic thermal expansion coefficient shall be selected as insert materials, such as aluminum, aluminum alloy and copper.
C. Apply a layer of rubber or polyurethane elastic buffer layer on the metal insert, and ensure that the coating does not melt during molding, which can reduce the shrinkage difference between the two.
D. Surface degreasing treatment of metal inserts can prevent stress cracking of products accelerated by grease.
E. The metal inserts shall be properly preheated.
F. The thickness of plastic around the metal insert shall be sufficient. For example, if the outer diameter of the insert is D and the plastic thickness around the insert is h, then the plastic thickness of the aluminum insert h ≥ 0.8D; For copper inserts, the plastic thickness h ≥ 0.9 D.
G. The metal insert shall be designed into a smooth shape, preferably with a fine rolling pattern.