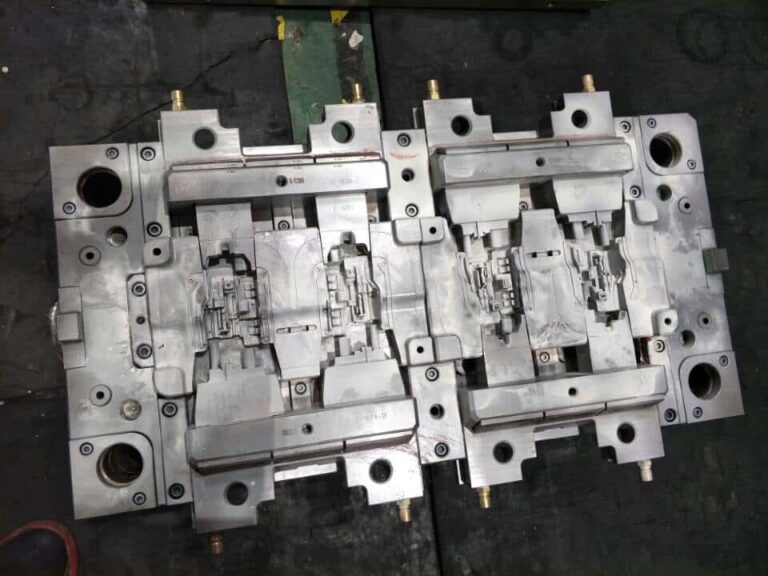
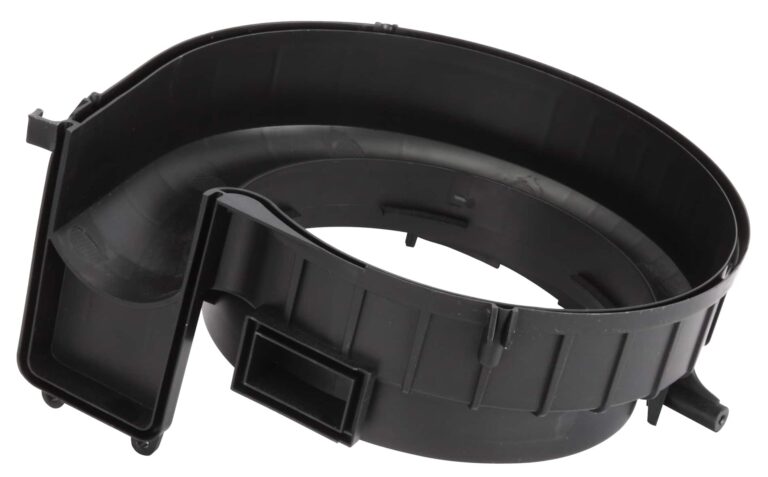
Injection molding cycle
Molding cycle: The molding cycle directly affects labor productivity and equipment utilization. Therefore, in the production process, the relevant time in the molding cycle should be shortened as much as possible on the premise of ensuring the quality. In the whole molding cycle, injection time and cooling time are the most important, which have a decisive impact on the quality of products.
The filling time in the injection time is directly inversely proportional to the filling rate, and the filling time in production is generally about 3-5 seconds. The pressure holding time in the injection time is the pressure time for the plastic in the mold cavity, which accounts for a large proportion in the entire injection time, generally about 20-120 seconds (up to 5-10 minutes for extra thick parts).

Before the melt at the gate is frozen, the holding time has an impact on the dimensional accuracy of the product. If it is later, it has no impact. The holding time also has the most favorable value. It is known that it depends on the material temperature, mold temperature, and the size of the sprue and gate. If the dimensions of the sprue and gate and the process conditions are normal, the pressure value with the lowest fluctuation range of the shrinkage of the product is usually taken as the criterion.
The cooling time mainly depends on the thickness of the product, the thermal and crystalline properties of the plastic, and the mold temperature. The end point of cooling time shall be based on the principle of ensuring that the products will not be changed during demoulding. The cooling time is generally about 30~120 seconds. It is unnecessary to have too long cooling time, which will not only reduce production efficiency, but also cause difficulty in demoulding for complex parts, and even produce demoulding stress when forced demoulding. Other times in the molding cycle are related to whether the production process is continuous and automatic, and the degree of continuity and automation.