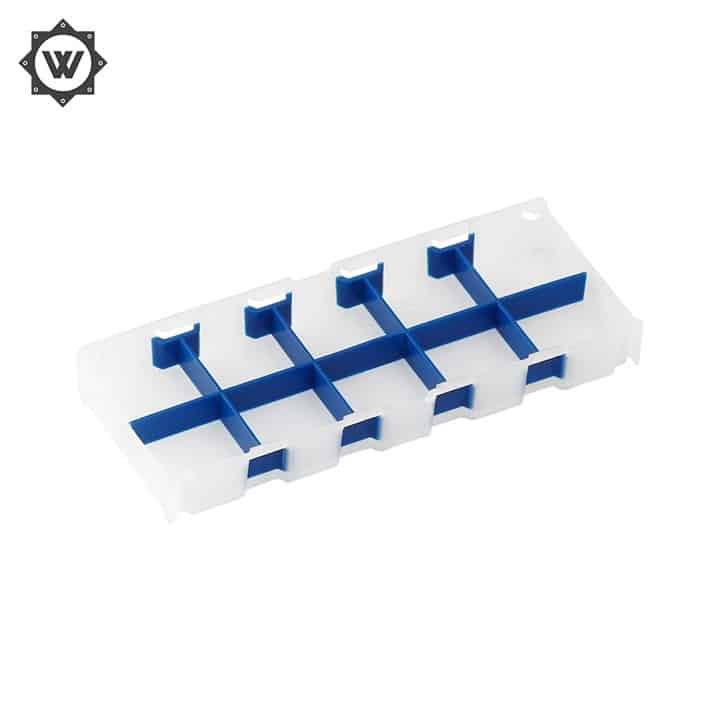
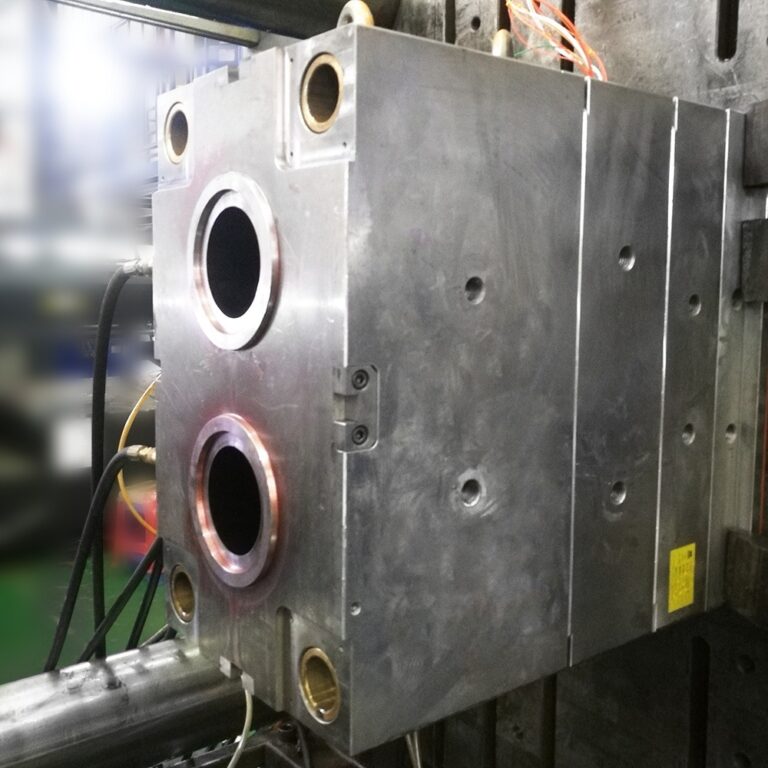
What Is “mold making”?
Mold Making refers to the processing of forming and blank making tools, in addition to shear molds and die cutting molds. Generally, the mold consists of upper mold and lower mold. Place the steel plate between the upper and lower molds, and realize the forming of materials under the action of the press. When the press is opened, the workpiece determined by the mold shape will be obtained or the corresponding waste materials will be removed. Workpieces as small as electronic connectors and as large as automobile instrument panels can be molded with molds.
Progressive die refers to a set of dies that can automatically move the workpieces from one station to another, and obtain the formed parts at the last station. Die processing technology includes: cutting die, blanking die, compound die, extrusion die, four slide rail die, progressive die, stamping die, die cutting die, etc.
2 Mold type
(1) Metal stamping die: continuous die, single die, compound die, drawing die
(2) Plastic molding mold: injection mold, extrusion mold, blister mold
(3) Die-casting die
(4) Forging die
(5) Powder metallurgy die
(6) Rubber mold

3 Mold processing flow
Blanking: front mold material, rear mold material, insert material, line position material and inclined jacking material;
Open frame: front mold frame, rear mold frame;
Coarsening: the front mold cavity is roughened, the rear mold cavity is roughened, and the parting line is roughened;
Copper male: front mold copper male, rear mold copper male, parting line corner clearing copper male;
Wire cutting: insert parting line, copper pin, inclined top sleeper position;
Computer gongs: precision gongs parting line, precision gongs back mold core;
Electric spark: front mold thick, copper male, male mold line angle cleaning, rear mold bone position, pillow position;
Drilling, pinhole, thimble; Die thimble hole water path hole processing line position, line position pressure pole;
Inclined jacking, double jacking needle and equipped with jacking needle.
4 Others
(1) Jacks, die pits, garbage nails (limit nails);
(2) Flying mode;
(3) Water inlet, stay head, spring and water conveyance;
(4) Save mold, polish, front mold, back mold bone position;
(5) Fine water structure, pull rod screw hook, spring
(6) Heat treatment, quenching and surface nitriding of important parts;
5 Mold software
UGNX, Pro/NC, CATIA, MasterCAM, SurfCAM, TopSolid CAM, SPACE-E, CAMWORKS, WorkNC, TEBIS, HyperMILL, Powermill, GibbsCAM, FEATURECAM, etc.
6 Basic characteristics
(1) A pair of molds with high processing accuracy requirements is generally composed of a female mold, a male mold and a mold base, and some may also be multi piece splicing modules. Therefore, the combination of upper and lower molds, the combination of insert and cavity, and the combination of modules all require high processing accuracy. The dimensional accuracy of precision dies is often up to μ Grade m.
(2) Some products, such as automobile panels, aircraft parts, toys and household appliances, have complex shapes and surfaces, which are composed of a variety of curved surfaces. Therefore, the mold cavity surface is very complex. Some surfaces must be treated mathematically.
(3) The production of small batch molds is not mass production. In many cases, only one pair is produced.
(4) Multiple working procedures Milling, boring, drilling, reaming, tapping and other working procedures are always used in die processing.
(5) The use of the repetitive production mould has a life span. When the use of a pair of dies exceeds their service life, new dies will be replaced, so the production of dies is often repetitive.
(6) Profiling processing mold production sometimes has no drawings or data, and profiling processing should be carried out according to the real object. This requires high copying accuracy and no deformation.
(7) The die materials are excellent. The main materials of high hardness dies are mostly made of high-quality alloy steel, especially the dies with long service life, which are often made of Crl2, CrWMn and other ledeburite steels. This kind of steel has strict requirements from blank forging, processing to heat treatment. Therefore, the preparation of processing technology can not be ignored, and heat treatment deformation is also a problem that needs to be seriously treated in processing.
According to the above characteristics, the machine tool shall be selected to meet the processing requirements as much as possible. For example, the CNC system should have strong functions, high machine precision, good rigidity, good thermal stability, profiling function, etc.
7 Processing Process Arrangement
(1) Bottom surface processing and processing quantity guarantee;
(2) Casting blank datum alignment, 2D and 3D profile allowance inspection;
(3) Rough machining of 2D and 3D profiles, machining of non installation and non working planes (including safety platform surface, buffer mounting surface, pressing plate plane and side datum plane);
(4) Before semi finishing, the side reference surface shall be correctly located to ensure accuracy;
(5) Semi finish 2D and 3D profiles, finish all kinds of installation working surfaces (including the installation surface and contact surface of the limit block, the installation surface and back side of the insert, the installation surface of the punch, the installation surface and back side of the waste cutter, the installation surface and contact surface of the spring, all kinds of travel limit working surfaces, the installation surface and back side of the wedge), semi finish all kinds of guide surfaces and guide holes, leave margin for finishing the process reference holes and height reference surfaces, and record the data;
(6) Inspect and recheck the machining accuracy;
(7) Bench worker inlaying process;
(8) Before finishing, align the datum plane of the process datum hole and check the allowance of the insert;
(9) Finish machining profile 2D and 3D, side punching profile and hole location, finish machining process datum hole and height datum, finish machining guide surface and guide hole;
(10) Check and recheck the machining accuracy.
8 Precautions
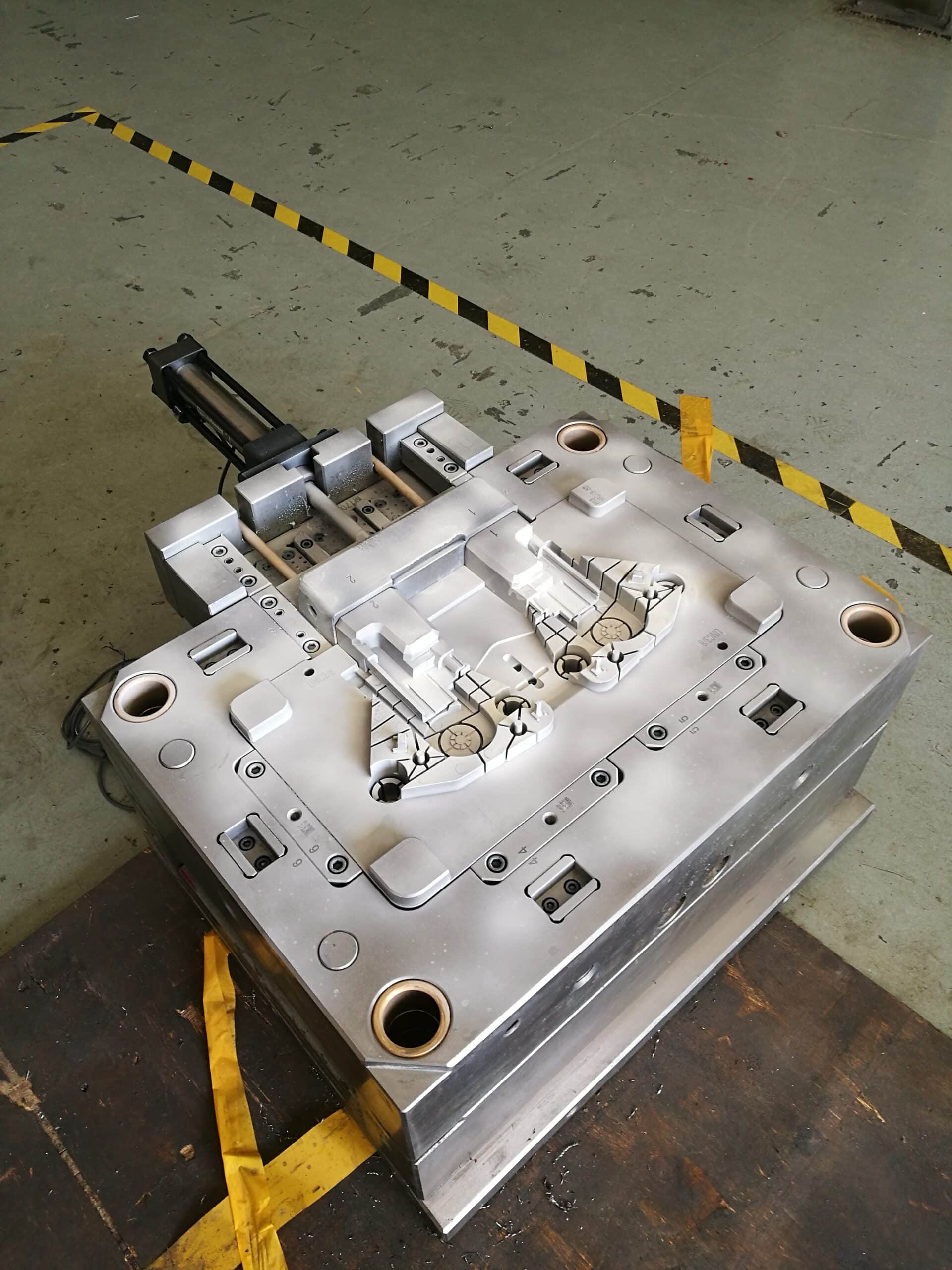

(1) The process preparation shall be concise and detailed, and the processing content shall be expressed numerically as far as possible;
(2) For the key and difficult points of processing, the process shall be specially emphasized;
(3) Where combined processing is required, the process expression is clear;
(4) When the insert needs to be processed separately, pay attention to the process requirements for processing accuracy;
(5) After combined processing, insert parts that need to be processed separately shall meet the benchmark requirements of process installation and separate processing during combined processing;
(6) The spring is the easiest to be damaged in die processing, so the die spring with long fatigue life should be selected.